Wireless Network Localization
Research summary
Location-awareness plays a crucial role in many wireless network applications, such as localization services in next generation cellular networks, search-and-rescue operations, logistics, and blue force tracking in battlefields. The global positioning system (GPS) is the most important technology to provide location-awareness around the globe through a constellation of 24 satellites. However, the effectiveness of GPS is limited in harsh environments, such as in buildings, in urban canyons, under tree canopies, and in caves, due to the inability of GPS signals to penetrate most obstacles. Hence, new localization techniques are required to meet the increasing need for accurate localization in such harsh environments.
Our research interests revolve around following directions:
Theoretical framework for cooperative relative localization
Beamspace direct localization
Tensor-based multipath estimation
Network localization and synchronization using full-duplex radios
Joint active and passive localization framework
Localization techniques based on polarization sensitive array
Bluetooth indoor localization algorithm design
Localizability analysis of large-scale networks
5G positioning system based on SRS signal
Representative research works
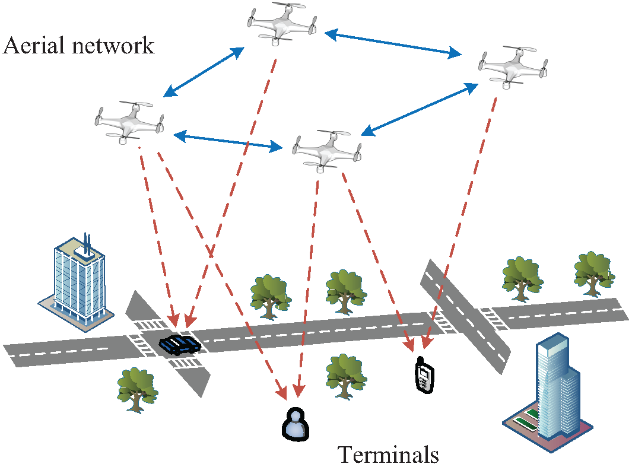 |
Relative localization: A theoretical analysis framework in terms of the constraint CRLB of EFIM is derived, and the geometry merging and geometry transforming algorithms for relative localization are designed. We further analyze the characteristics of resource allocation for relative localization, and design a corresponding resource allocation algorithm.
|
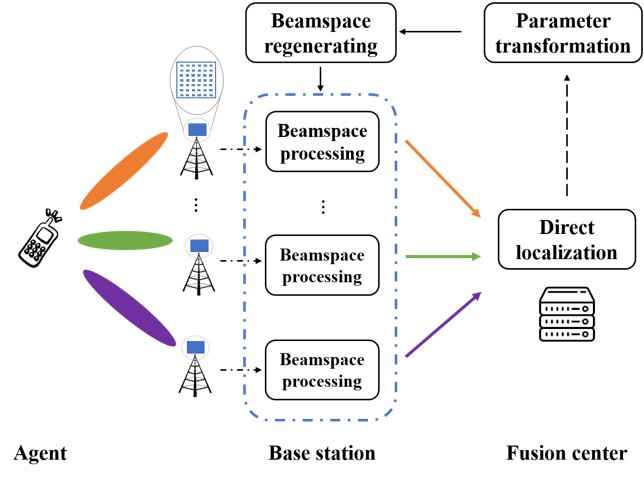 |
Beamspace direct localization: We prove that the high-dimensional array signal can be represented in a low-dimensional beamspace without information loss and further propose a robust beamspace design strategy.
|
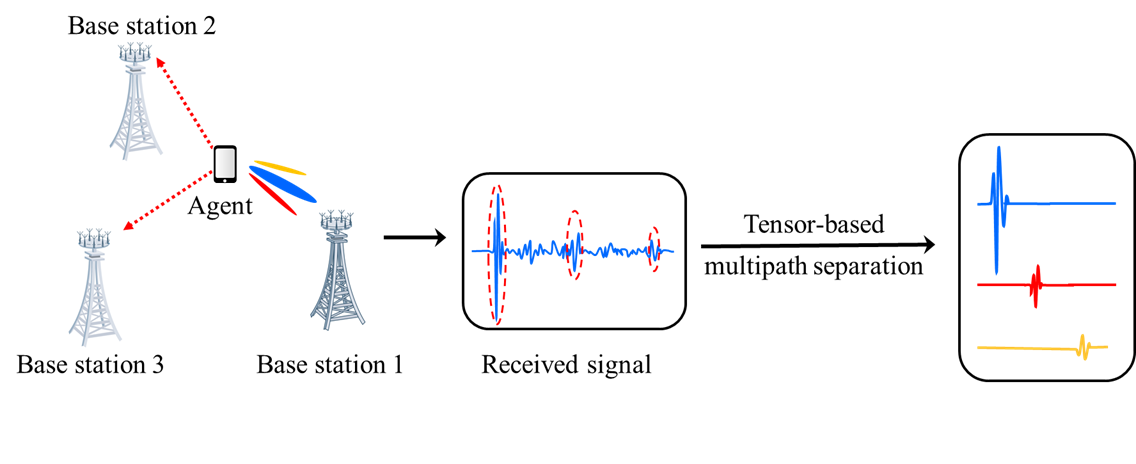 |
Tensor-based network localization: We explore the inherent structure in the measurements and the uniqueness of tensor factorization to achieve high-accuracy network localization in multipath environments. By formulating the localization problem as a low-rank tensor decomposition problem, we develop a tensor decomposition-based direct localization algorithm using the designed beamspaces to significantly enhance the estimation accuracy with low complexity and data association-free methods.
|
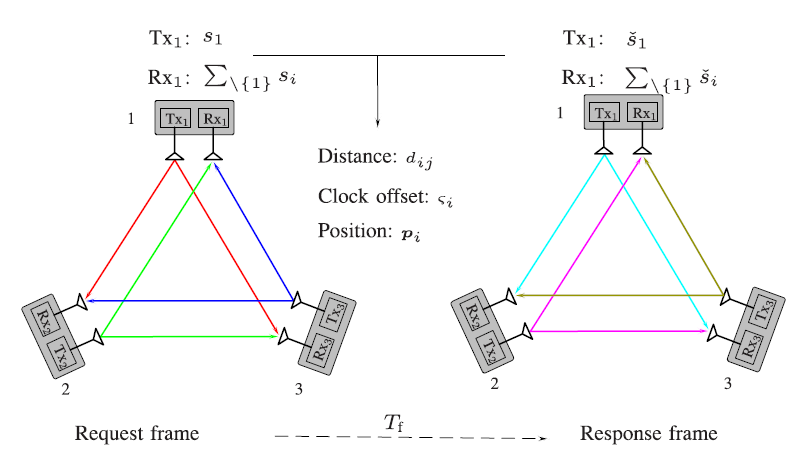 |
Network localization and synchronization using full-duplex radios: We propose NLS schemes using full-duplex radios, where internode distances and clock offsets can be estimated through only two frames of transmission.
|
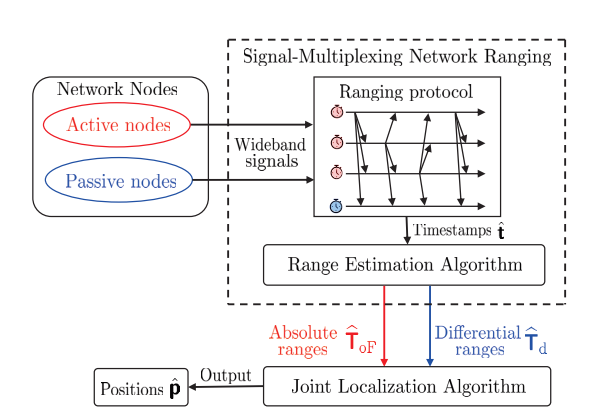 |
Joint active and passive localization framework: We design a network ranging method with a minimum number of signal transmissions.
|
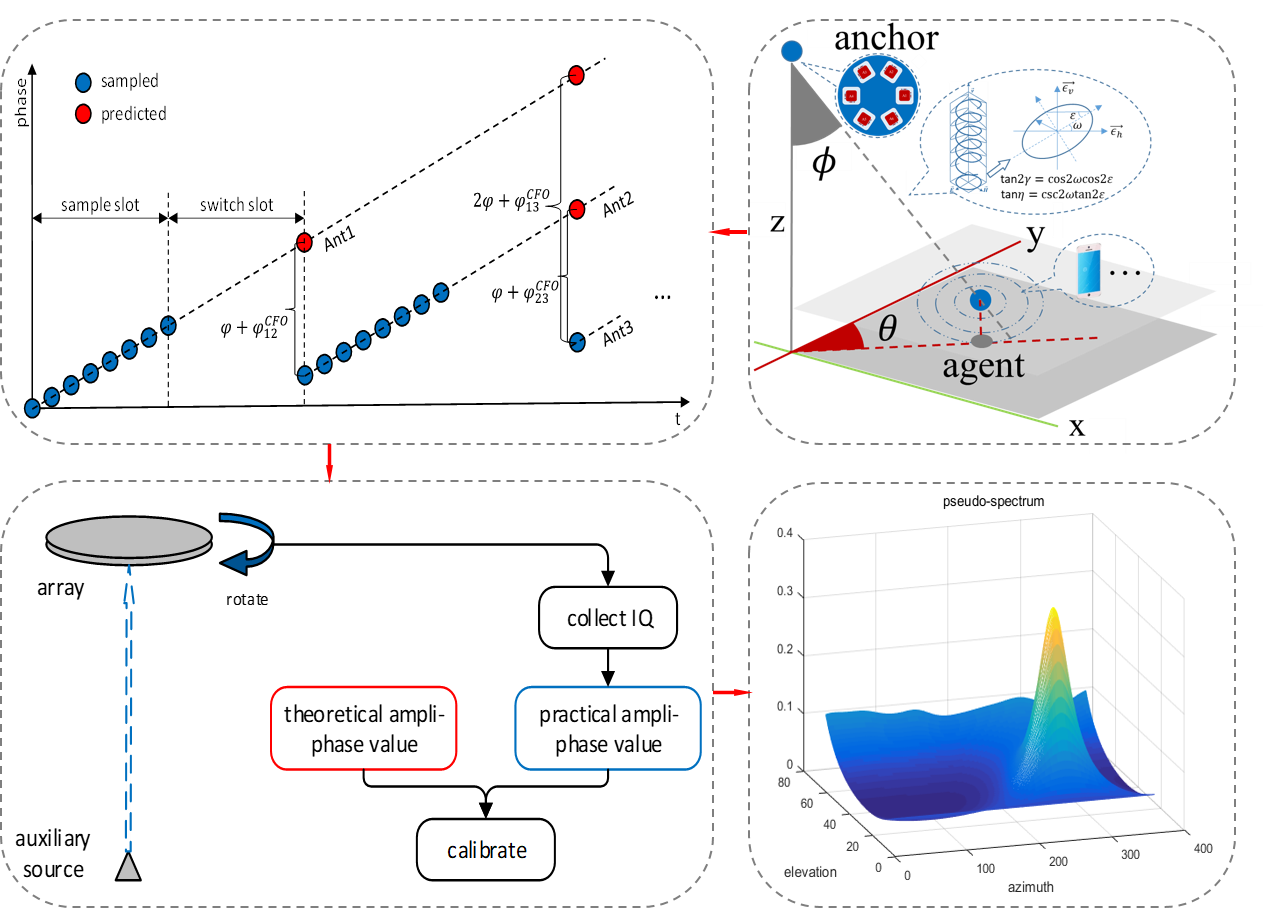 |
Polarization-sensitive-array-based BLE localization system: We design and implement a real-time single anchor polarization-sensitive-array-based BLE localization system using angular information, which achieves a median accuracy of 30 cm.
|
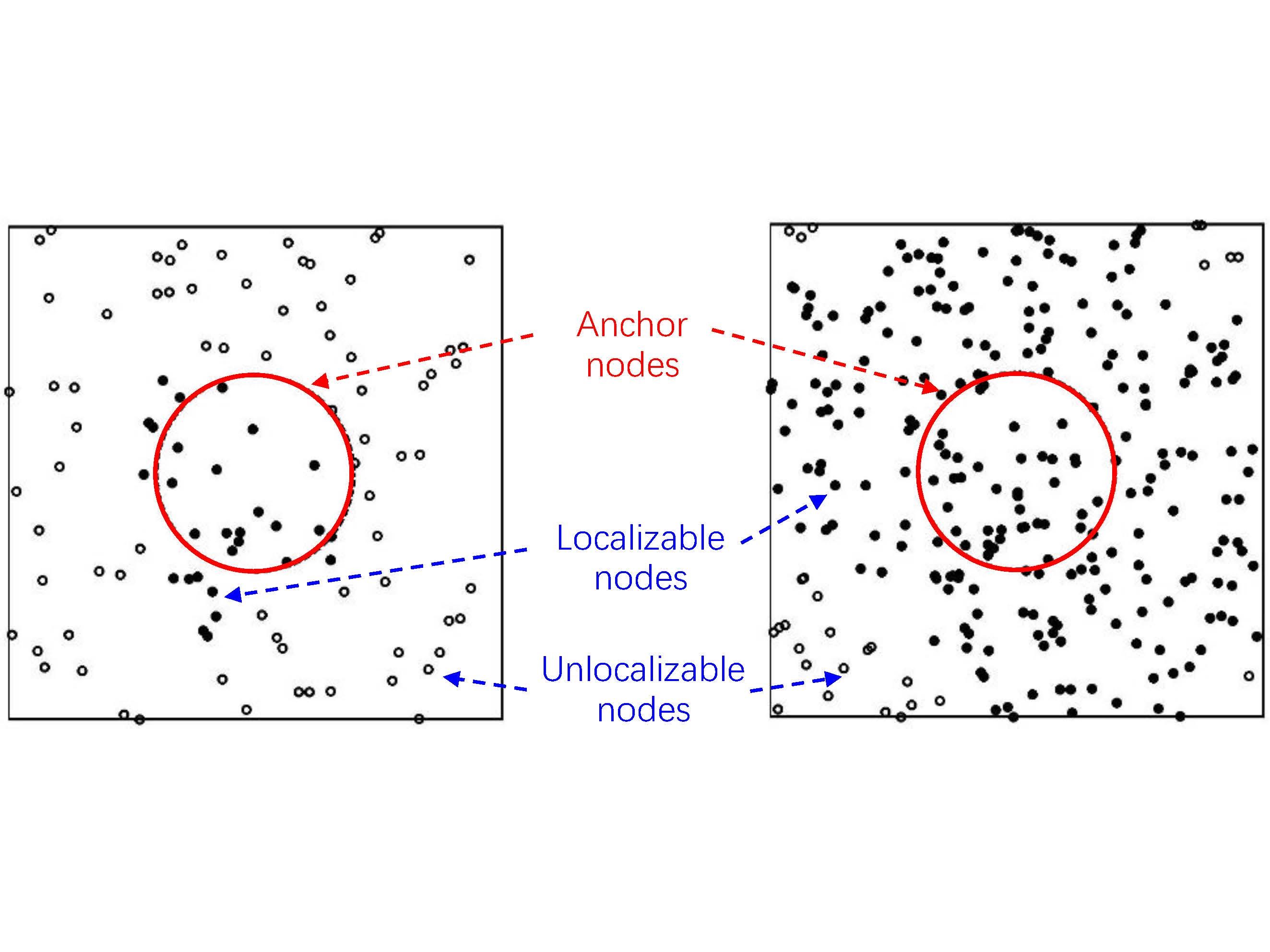 |
We introduce the Percolation Theory in the cooperative network localization problem, prove the existence of the critical node intensity for the localizability of large-scale network.
|
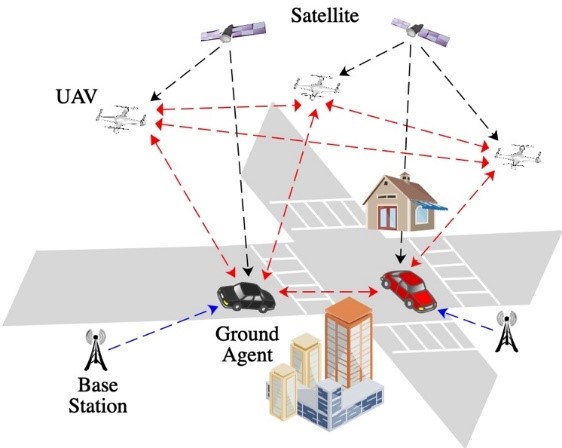 |
We propose a 5G cooperative localization scheme and a distributed cooperative localization algorithm based on maximum likelihood principle. Next, the proposed scheme and algorithm are implemented and simulated by using MATLAB. The superiority of the proposed scheme is verified by comparing with the theoretical limit of positioning error. Finally, we explore the factors affecting the stability of the cooperative localization technology in 5G vehicle networks, and provide ideas for the future research of localization scheme in vehicle networks.
|