|
Cooperative Multi-agent Networks
Research summary
Multi-agent networks have exhibited increasingly prominent features of self-adaptation and collaboration due to the rapid development of information technology. The study of cooperative sensing and communication for autonomous unmanned systems, as well as cooperative control and optimization decision-making, and the formation of an innovative theoretical system framework for autonomous intelligent unmanned systems are of great significance to the growth of smart industries and the cultivation of smart society. Collaboration capability for multi-agent mobile networks has huge application potential and practical value in both military and civilian scenarios.
We are focusing on the following research directions:
Cooperative detection in mobile multi-agent networks
Large-scale cooperative localization
Joint localization and formation of multi-agent networks
Cooperative visual perception in multi-agent networks
Multi-agent cooperative formation based on integrated localization and control
Cooperative scheduling of high-dynamic intelligent systems
Deep reinforcement learning algorithm for multi-agent networks
Representative works
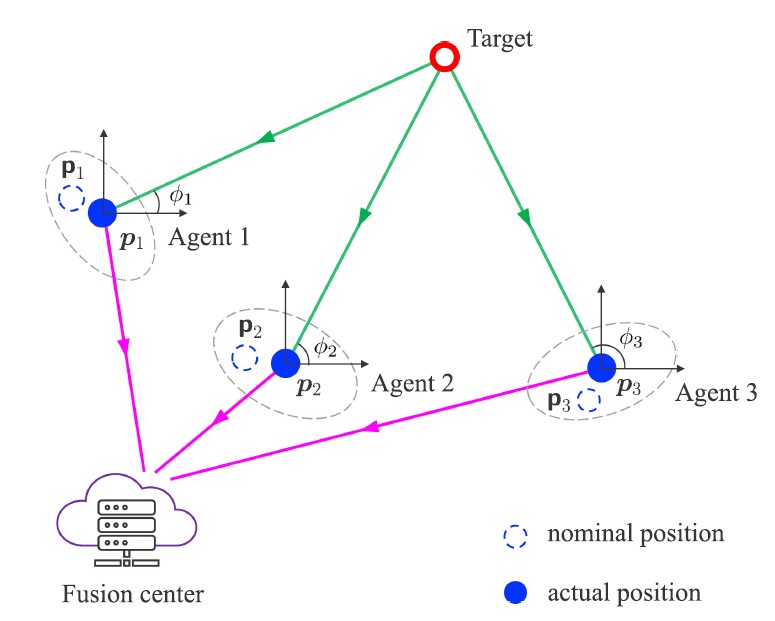 |
Cooperative detection in mobile multi-agent networks: We propose a cooperative detection scheme for non-cooperative targets, and design a GLRT detector to realize joint position self-calibration and target detection.
K. Gu, Y. Wang, and Y. Shen, ‘‘A quasi-coherent detection framework for mobile multi-agent networks,‘‘ IEEE Trans. Signal Process., vol. 69, pp. 6416-6430, Oct. 2021.
K. Gu, Y. Wang, and Y. Shen, “Cooperative detection by multi-agent networks in the presence of position uncertainty,” IEEE Trans. Signal Process., vol. 68, pp. 5411-5426, Sep. 2020.
K. Gu, J. Wang, Y. Wang, and Y. Shen, ‘‘On the performance of multi-agent detection in mobile delay-sensitive networks,‘‘ in Proc. IEEE Global Commun. Conf., Madrid, Spain, Dec. 2021, pp. 1-6.
|
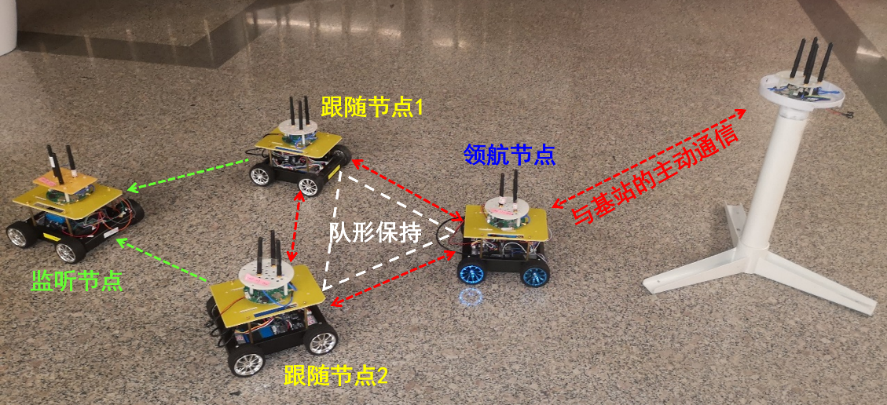 |
Joint localization and formation of multi-agent networks: We design a new index reflecting the formation performance. The formation performance when there are statistical errors in positioning and control is analyzed.
X. Li, Y. Wang, K. Ma, L. Xu, Z. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Wang, and Y. Shen, ‘‘A cooperative relative localization system for distributed multi-agent networks,‘‘ IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., 2023, Early Access.
C. Pan, Y. Yan, Z. Zhang, and Y. Shen, ‘‘Flexible formation control using Hausdorff distance: a multi-agent reinforcement learning approach,‘‘ in Proc. Eur. Signal Process. Conf., Belgrade, Serbia, Sep. 2022, pp. 1-5.
Y. Yan, X. Li, X. Qiu, J. Qiu, J. Wang, Y. Wang, and Y. Shen, ‘‘Relative distributed formation and obstacle avoidance with multi-agent reinforcement learning,‘‘ in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Philadelphia, PA, United States, May 2022, pp. 1-6.
X. Li, K. Ma, J. Wang, and Y. Shen, “An integrated design of cooperative localization and motion control,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Commun. in China, Changchun, China, Aug. 2019, pp. 1-5.
|
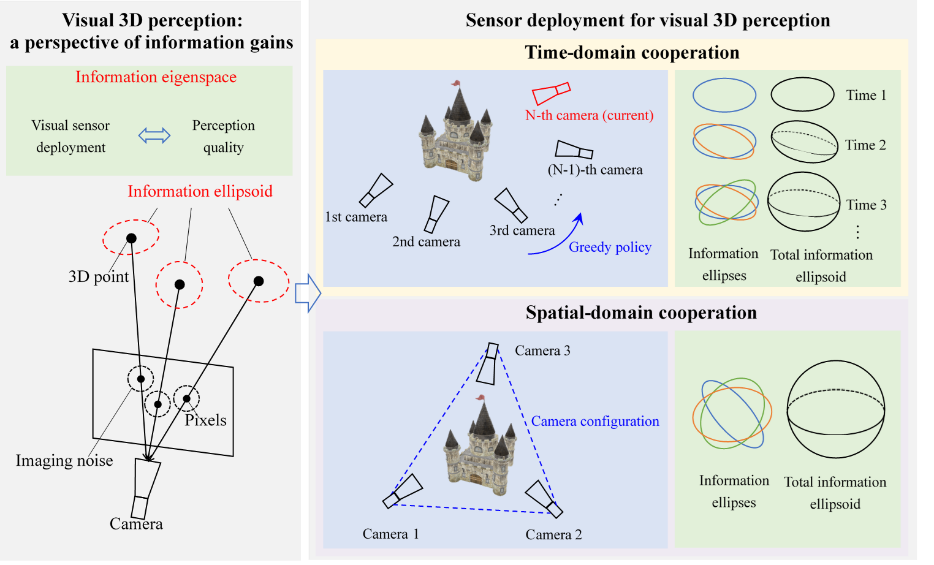 |
We propose a statistical framework for cooperative visual 3D perception in multi-agent networks. A metric based on statistical analysis is designed to evaluate the dependence of reconstruction quality on visual sensor deployment. The temporal and spatial cooperation for optimal sensor deployment is exploited.
Q. An, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, and Y. Shen, ‘‘Information-based bit allocation for cooperative visual sensing in vehicular networks,‘‘ IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., vol. 72, no. 2, pp. 2365-2380, Feb. 2023.
Q. An and Y. Shen, ‘‘On the information coupling and propagation of visual 3D perception in vehicular networks with position uncertainty,‘‘ IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., vol. 70, no. 12, pp. 13 325-13 339, Oct. 2021.
Q. An, Y. Wang, and Y. Shen, “Sensor deployment for visual 3D perception: A perspective of information gains,” IEEE Sensors J., vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 8464-8478, Mar. 2021.
|
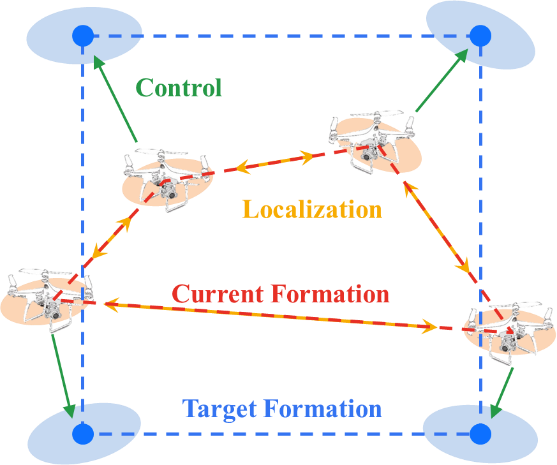 |
A distributed formation algorithm based on the integrated framework of localization and control is proposed, which can achieve near-optimal accuracy (close to the fundamental limit), and has strong robustness to measurement and control noise.
K. Ma and Y. Shen, “High-accuracy 3D relative formation via integrated localization and control,” IEEE Trans. Signal Process., submitted.
K. Ma and Y. Shen, “Distributed formation algorithm based on integrated localization and control,” in Proc. IEEE Global Telecomm. Conf., Taipei, China, Dec. 2020, pp. 1-5.
|
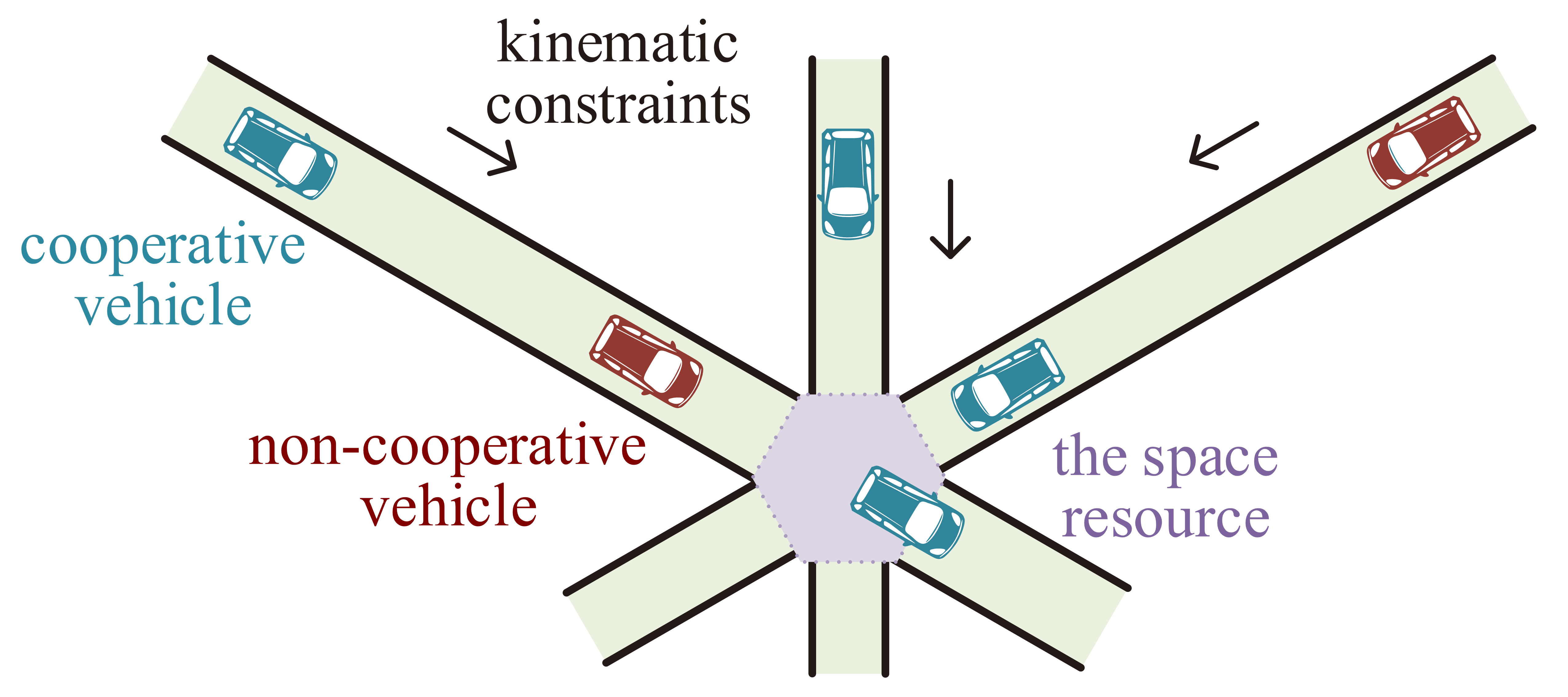 |
We establish a distributed trajectory planning framework in multi-agent inertially-constrained scheduling systems with both cooperative and non-cooperative agents, which can achieve a safe and robust performance against the trajectory uncertainty of the non-cooperative agents and can exploit the benefit of cooperation to improve the efficiency.
F. Yang and Y. Shen, ’'A minimax framework for two-agent scheduling with inertial constraints,’’ IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 23, no. 12, pp. 24401-24413, Dec. 2022.
F. Yang and Y. Shen, ’'A minimax scheduling framework for inertially-constrained multi-agent systems,’’ IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 23, no. 12, pp. 24414-24427, Dec. 2022.
F. Yang and Y. Shen, ’'Distributed scheduling at non-signalized intersections with mixed cooperative and non-cooperative vehicles,’’ IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., 2023. vol. 72, no. 6, pp. 7123-7136, Jun. 2023.
|
|




